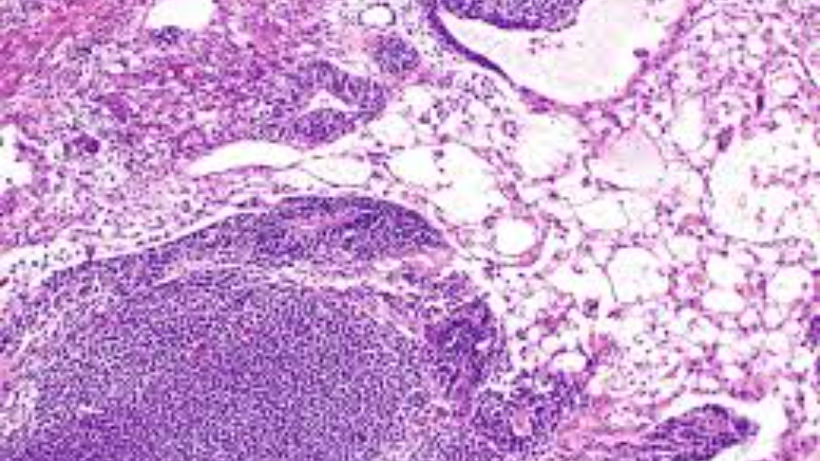
Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors: Symptoms, Treatment and all
24 Oct, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamOvarian germ cell tumors, though uncommon, represent a distinctive group of neoplasms arising from reproductive cells in the ovaries. These tumors, ranging from benign to malignant, predominantly affect young women. This brief overview aims to explore the symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options for ovarian germ cell tumors, offering insights into this relatively rare yet important facet of ovarian health
Transform Your Beauty, Boost Your Confidence
Find the right cosmetic procedure for your needs.

We specialize in a wide range of cosmetic procedures

What is the ovarian germ cell tumor?
In the context of a woman's reproductive system, particularly the ovaries, Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors refer to abnormal growths or lumps. These growths, while uncommon, can manifest within the reproductive organs.
In simple terms, these tumors arise when the usual pattern of cell growth in the ovaries deviates. Normally well-behaved cells undergo abnormal proliferation, resulting in the formation of tumors. The precise reasons for this deviation are not entirely clear, contributing to the complexity of these cases.
The infrequency of Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors is noteworthy. This rarity underscores the general smooth functionality of our reproductive system. In a way, it acts as a reminder that our bodies typically operate without disruptions. The uncommon nature of these tumors invites exploration into the less understood facets of our reproductive health.
Most popular procedures in India
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
ANGIOGRAM
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

ASD Closure
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

OGCTs are rare tumors, accounting for about 2% to 3% of all ovarian cancers.
They are most common in young women, with a median age of diagnosis at 16 to 20 years.
Black and Hispanic women are more likely to develop OGCTs than white women.
What are the various types of ovarian germ cell tumors?
Ovarian germ cell tumors are a diverse group of tumors that arise from the germ cells of the ovary, the cells that give rise to eggs. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). The various types of ovarian germ cell tumors include:
1. Dysgerminoma:
Dysgerminomas are the most common malignant germ cell tumors of the ovary. They often occur in adolescents and young women. Dysgerminomas are highly sensitive to radiation and chemotherapy, and they have a favorable prognosis when diagnosed and treated early.
2. Endodermal Sinus Tumor (Yolk Sac Tumor
Yolk sac tumors are aggressive malignant germ cell tumors that often contain structures resembling the yolk sac of an embryo. They are more common in young girls and adolescents. Elevated levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in the blood are often associated with yolk sac tumors.
3. Immature Teratoma:
Immature teratomas are tumors that contain tissue from all three germ cell layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm). They are considered malignant and are more common in adolescents and young women. The term "immature" indicates that the tissues within the tumor are not fully differentiated.
4. Struma Ovarii:
Struma ovarii is a specialized type of ovarian germ cell tumor that predominantly consists of thyroid tissue. In some cases, the thyroid tissue can become cancerous (struma ovarii with malignant transformation). Most struma ovarii are benign, and they are often discovered incidentally during surgery.
5. Teratoma (Mature and Immature):
Teratomas are tumors that can contain a variety of tissues derived from the three germ cell layers. Mature teratomas are typically benign and may contain hair, teeth, and other well-differentiated tissues. Immature teratomas, as mentioned earlier, are considered malignant.
6. Choriocarcinoma:
Choriocarcinoma is a very rare and aggressive malignant germ cell tumor that can occur in the ovaries. It is characterized by the presence of cells that produce human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone associated with pregnancy. Choriocarcinoma is highly responsive to chemotherapy.
7. Mixed Germ Cell Tumors:
Some ovarian germ cell tumors may contain a combination of different cell types, leading to mixed germ cell tumors. These tumors can include elements of dysgerminoma, yolk sac tumor, and teratoma, among others.
Stages of ovarian germ cell tumors (OGCTs)
The stages of ovarian germ cell tumors (OGCTs) are as follows:
Stage IA
- Cancer is found in a single ovary or fallopian tube.
- The tumor is small and has not spread beyond the ovary or fallopian tube.
Stage IB
- Cancer is found in both ovaries or fallopian tubes.
- The tumor may be small or large, but it has not spread beyond the ovaries or fallopian tubes.
Stage IC
- Cancer is found in one or both ovaries or fallopian tubes and has spread to one of the following:
- The surface of the ovary has ruptured.
- Cancer cells are found in the fluid in the abdomen or pelvis.
- Cancer cells are found in the tissue lining the abdomen (peritoneum).
Stage II
- Cancer has spread to other organs in the pelvis, such as the uterus or cervix.
- Cancer may also have spread to the tissue lining the abdomen (peritoneum).
Stage III
- Cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the abdomen or pelvis.
- Cancer may also have spread to the tissue lining the abdomen (peritoneum).
Stage IV
- Cancer has spread to other organs outside of the abdomen, such as the lungs, liver, or brain.
The stage of an OGCT is determined after surgery to remove the tumor. The surgeon will examine the tumor and the surrounding tissues to see if cancer has spread. The surgeon may also order other tests, such as imaging scans, to check for cancer in other parts of the body.
What are the symptoms and signs associated with ovarian germ cell tumors?
Let's explore the various aspects of symptoms associated with ovarian germ cell tumors.
- Abdominal or Pelvic Pain:
- Persistent, dull, or sharp pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis, often not relieved by usual remedies.
- Abdominal Swelling or Bloating:
- Noticeable enlargement of the abdomen, possibly leading to a feeling of fullness or tightness.
- Changes in Menstrual Patterns:
- Irregular menstrual cycles, including missed periods or unusually heavy or prolonged bleeding.
- Painful Intercourse:
- Discomfort or pain during sexual intercourse, which may be a result of the tumor affecting pelvic structures.
- Urinary Symptoms:
- Increased frequency of urination, with a persistent sense of urgency.
- Potential difficulty emptying the bladder completely.
- Gastrointestinal Symptoms:
- Nausea or vomiting, which may be unrelated to other common causes.
- Changes in bowel habits, such as persistent constipation.
- Fatigue:
- Generalized tiredness, weakness, or lack of energy.
- Unexplained Weight Loss:
- Significant and unintentional weight loss without changes in diet or physical activity.
- Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding:
- Vaginal bleeding between periods, after menopause, or any abnormal bleeding that is not associated with the menstrual cycle.
- Pelvic Pressure:
- A sensation of fullness or pressure in the pelvic area, often accompanied by discomfort.
- Painful Ovulation:
- Pain or discomfort during ovulation, which may be cyclic in nature.
- Presence of Abdominal Mass:
- Palpable mass or swelling in the abdominal or pelvic region, detected during self-examination or by a healthcare professional.
- Elevated Tumor Markers:
- Elevated levels of tumor markers, such as alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) or beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (?-hCG), in blood tests. These markers may be used to assess the presence of certain ovarian germ cell tumors.
Causes of ovarian germ cell tumors
Let's delve into the factors that contribute to the development of ovarian germ cell tumors.
1. Genetic Factors:
In some cases, there may be a genetic predisposition to ovarian germ cell tumors. Certain genetic conditions, such as Swyer syndrome or familial ovarian cancer syndromes, may increase the risk.
2, Congenital Conditions:
Women with certain congenital conditions, such as gonadal dysgenesis, may have an increased risk of developing ovarian germ cell tumors.
3. Family History:
A family history of ovarian germ cell tumors or ovarian cancer may elevate the risk. Women with first-degree relatives (mother, sister, daughter) who have had ovarian germ cell tumors or ovarian cancer may be at a higher risk.
4. Age:
Ovarian germ cell tumors often occur in younger women, with the peak incidence in the second and third decades of life.
5. Race and Ethnicity:
There may be variations in the incidence of ovarian germ cell tumors among different racial and ethnic groups.
6. Reproductive Factors:
Factors related to reproductive history may influence the risk. Women who have never been pregnant or those who have difficulty conceiving may have a slightly higher risk.
7. Menstrual History:
There may be a correlation between menstrual history and the risk of ovarian germ cell tumors. Early onset of menstruation (menarche) or late menopause may be associated with a higher risk.
8. Environmental Factors:
While the evidence is not conclusive, exposure to certain environmental factors or toxins may be associated with an increased risk. Research in this area is ongoing.
9. Radiation Exposure:
Exposure to ionizing radiation, especially at a young age, may be a risk factor for the development of ovarian germ cell tumors.
10. Prior History of Cancer:
Women who have a history of certain cancers, such as breast cancer or other ovarian tumors, may have an increased risk.
How is the diagnosis of ovarian germ cell tumors conducted?
Let's explore the diagnostic methods employed in identifying ovarian germ cell tumors.
The diagnosis of ovarian germ cell tumors typically involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, imaging studies, and laboratory tests. Here is an overview of the diagnostic process:
1. Medical History and Physical Examination:
- The healthcare provider begins by taking a detailed medical history, including any symptoms the patient may be experiencing.
- A pelvic examination is conducted to check for any abnormalities, such as ovarian masses or swelling.
- Ultrasound: Transvaginal ultrasound is often the initial imaging study used to visualize the ovaries and detect any abnormalities. This imaging technique can help identify the size, location, and characteristics of ovarian tumors.
- CT Scan or MRI: In some cases, a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be recommended to obtain more detailed images of the pelvic and abdominal structures. These imaging studies can help determine the extent of the tumor and whether it has spread to nearby organs.
- Tumor Markers: Blood tests may be conducted to measure levels of certain tumor markers associated with ovarian germ cell tumors. Common tumor markers include alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (?-hCG). Elevated levels of these markers can suggest the presence of a germ cell tumor.
- Biopsy:
- Surgical Biopsy: A definitive diagnosis often requires a surgical biopsy, where a sample of the tumor is removed for examination. This is typically done through a surgical procedure such as laparoscopy or laparotomy.
- Frozen Section Analysis: During surgery, a frozen section analysis may be performed. This is a rapid microscopic examination of the tissue to provide preliminary information about the nature of the tumor. However, a formal pathology report is usually needed for a comprehensive diagnosis.
- The biopsy sample is sent to a pathologist who examines it under a microscope. The pathologist assesses the type of tumor, its grade (degree of abnormality), and whether it is benign or malignant.
- Staging:
- If the tumor is determined to be malignant, staging is performed to assess the extent of spread. Staging may involve additional imaging studies and examination of other pelvic and abdominal structures
- In some cases, genetic testing may be recommended, especially if there is a family history of certain genetic conditions associated with an increased risk of ovarian germ cell tumors.
What treatment options are available for ovarian germ cell tumors?
Let's explore the various treatment avenues for ovarian germ cell tumors. The treatment for ovarian germ cell tumors depends on several factors, including the type of tumor, its stage, and the overall health of the patient. Treatment may involve surgery, chemotherapy, and sometimes radiation therapy. Here is an overview of the treatment options in detail:
1. Surgery:
- Oophorectomy: Surgical removal of the affected ovary or ovaries is often the initial step. In some cases, both ovaries may need to be removed. The surgeon may also remove the uterus, fallopian tubes, and nearby lymph nodes, depending on the extent of the disease.
- Fertility-Sparing Surgery: In certain cases, particularly in young women who wish to preserve fertility, surgeons may perform fertility-sparing surgery. This involves removing only the affected ovary or part of the ovary while sparing the uterus and the other ovary.
- Chemotherapy is commonly used to treat ovarian germ cell tumors. It involves the use of drugs that kill rapidly dividing cells, including cancer cells. Chemotherapy may be administered before or after surgery, depending on the stage and type of the tumor.
- The specific chemotherapy drugs used may include a combination of cisplatin, bleomycin, and etoposide. The choice of drugs and the duration of treatment depend on the characteristics of the tumor.
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. It may be used in some cases, particularly if there are residual cancer cells after surgery or if the tumor is not responding well to chemotherapy.
- Radiation therapy is less commonly used for ovarian germ cell tumors compared to other types of ovarian cancer.
- After completing initial treatment, patients will undergo regular follow-up appointments to monitor their health. These visits may include physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging studies to detect any signs of recurrence or new cancers.
- Long-term follow-up is essential to address potential late effects of treatment, monitor for the development of second cancers, and provide support for any psychological or emotional challenges.
- Clinical Trials:
- Participation in clinical trials may be an option for some patients. Clinical trials explore new treatments or combinations of treatments to improve outcomes for individuals with ovarian germ cell tumors.
How can we help with the treatment?
If you're on the lookout for treatment in India, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, UAE, and Turkey, let Healthtrip be your compass. We will serve as your guide throughout your medical treatment. We'll be by your side, in person, even before your medical journey commences. The following will be provided to you:
- Connect with renowned doctors from a network spanning 35+ countries and access the world's largest health travel platform.
- Collaboration with 335+ top hospitals , including Fortis and Medanta.
- Comprehensive treatments from Neuro to Cardiac to Transplants, Aesthetics, and Wellness.
- Post-treatment care and assistance.
- Teleconsultations at $1/minute with leading surgeons.
- Trusted by 44,000+ patients for appointments, travel, visa, and forex assistance.
- Access top treatments and packages, such as Angiograms and many more.
- Gain insights from genuine patient experiences and testimonials.
- Stay updated with our medical blog.
- 24/7 unwavering support, from hospital formalities to travel arrangements or emergencies.
- Pre-scheduled specialist appointments.
- Prompt emergency assistance, ensuring safety.
Our success stories
What factors contribute to the risk of ovarian germ cell tumors?
- Genetic factors contribute to ovarian germ cell tumors.
- Inherited genetic mutations can increase susceptibility.
- Familial history is a significant risk factor.
- Close relatives with ovarian germ cell tumors elevate the risk.
- Specific genetic mutations, like BRCA1 and BRCA2, may be linked to higher risk.
- Ovarian germ cell tumors are common in adolescents and young adults.
- Higher risk within the reproductive age range.
- Primarily affect individuals with ovaries (females).
- Extremely rare in males but not entirely non-existent.
What complications might arise from the treatment of ovarian germ cell tumors?
Let's outline the potential complications associated with ovarian germ cell tumors.
- Spread of the Tumor:
- Metastasis to nearby organs (uterus, fallopian tubes, lymph nodes).
- Advanced tumors may spread to distant organs like the liver or lungs.
- Infertility:
- Treatment can impact fertility.
- Difficulty conceiving naturally after treatment.
- Hormonal Imbalances:
- Disruption of normal hormonal balance.
- Symptoms include irregular menstrual cycles and changes in libido.
- Chemotherapy Side Effects:
- Nausea, vomiting, fatigue.
- Hair loss and increased infection risk.
- Surgical Complications:
- Risks include infection, bleeding, and anesthesia-related complications.
- Surgical removal of ovaries or uterus may be necessary.
- Psychological and Emotional Impact:
- Cancer diagnosis can lead to anxiety and depression.
- Emotional challenges during and after treatment.
- Recurrence:
- Risk of cancer returning despite successful treatment.
- Regular follow-up care is essential.
- Premature Menopause:
- Removal of ovaries may lead to premature menopause.
- Symptoms include hot flashes and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Risk of Second Cancers:
- Some treatments may increase the risk of other cancers.
- Consideration for long-term survivorship.
Preventive Measures
Let's outline the preventive measures for ovarian germ cell tumors.
- Regular Health Check-ups:
- Routine gynecological check-ups can help in the early detection of any abnormalities or changes in the ovaries.
- Genetic Counseling:
- Women with a family history of ovarian germ cell tumors or ovarian cancer may consider genetic counseling to assess the potential risk and discuss preventive strategies.
- Reproductive Health:
- Maintaining reproductive health through regular gynecological care and addressing any reproductive concerns may have indirect benefits.
- Healthy Lifestyle:
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, contributes to overall well-being.
- Avoiding Radiation Exposure:
- Minimizing exposure to ionizing radiation, especially during medical procedures, may be beneficial.
- Environmental Awareness:
- Staying informed about environmental factors and minimizing exposure to potential toxins, although the direct link to ovarian germ cell tumors is not well-established.
- Early Detection and Prompt Treatment:
- Being aware of the symptoms associated with ovarian germ cell tumors and seeking prompt medical attention for any persistent or concerning symptoms.
What are the survival rates and prognosis for ovarian germ cell tumors?
The survival rates and prognosis for ovarian germ cell tumors are very good, especially when the cancer is diagnosed and treated early. The five-year survival rate for all stages of ovarian germ cell tumors is about 95%. The survival rate is even higher for women with early-stage disease, with a five-year survival rate of 99% for stage 1 tumors.
The prognosis for ovarian germ cell tumors depends on a number of factors, including:
- The stage of the cancer at diagnosis
- The type of germ cell tumor
- The patient's age and overall health
- The patient's response to treatment
Women with early-stage ovarian germ cell tumors have a very good prognosis. Most women with early-stage disease will be cured with surgery alone. Women with more advanced disease may need additional treatment with chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. However, even women with advanced-stage disease have a good chance of survival, with a five-year survival rate of about 70%.
Fertility is a major concern for many women with ovarian germ cell tumors. The good news is that most women with ovarian germ cell tumors will be able to preserve their fertility. Fertility-sparing surgery is often possible, and many women are able to have children after treatment.
If you have been diagnosed with ovarian germ cell tumor, it is important to talk to your doctor about your prognosis and treatment options. Your doctor can help you develop a treatment plan that is right for you and your individual needs.
Ovarian germ cell tumors, though rare, are distinct growths in the ovaries, including types like dysgerminomas, yolk sac tumors, teratomas, and endodermal sinus tumors. Their rarity underscores the usually smooth functioning of our reproductive system. Comprehending their characteristics, risk factors, and treatment options is pivotal for effective management.
Future Directions: Looking ahead, ongoing research is poised to uncover more about genetic and environmental influences on ovarian germ cell tumors. Advances in diagnostics may improve early detection, enhancing prognoses. Personalized medicine's emergence offers tailored treatments, optimizing outcomes, preserving fertility, and elevating overall quality of life for those impacted by these tumors.
In this journey, collaboration among researchers, healthcare professionals, and patients promises ongoing progress, unraveling complexities, and refining strategies for diagnosis and treatment.
Wellness Treatment
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
