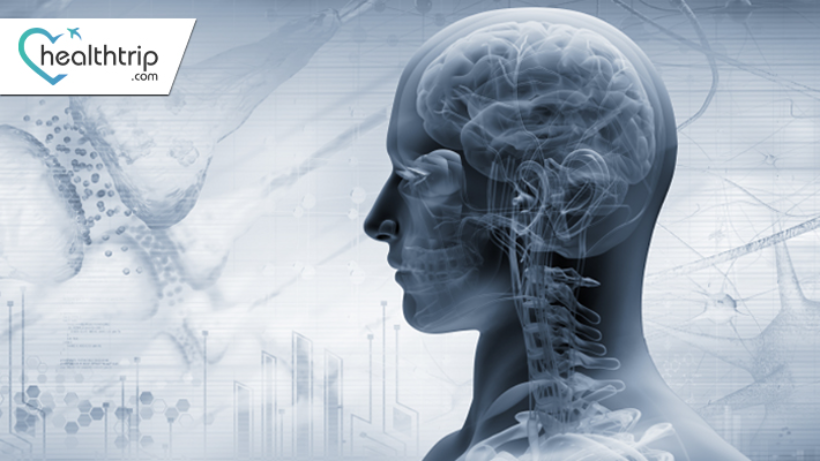

Vagus Nerve Stimulation Explained
26 Oct, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamIn the vast realm of medical marvels, few treatments have as much untapped potential as Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS). If you're unfamiliar with this groundbreaking procedure, you're in for an enlightening ride. VNS is not just a treatment; it's a testament to how deeply interconnected our body systems truly are. Dive in with us as we explore what VNS is, why it's performed, its immense benefits, and the latest advancements in this fascinating field.
VNS is a medical procedure wherein small electrical impulses are delivered to the vagus nerve, a crucial nerve that travels from the brain through the neck and into the chest and abdomen. The nerve plays a pivotal role in controlling mood, heart rate, digestion, and other essential functions. By stimulating this nerve, VNS can impact and regulate various body systems.
Transform Your Beauty, Boost Your Confidence
Find the right cosmetic procedure for your needs.

We specialize in a wide range of cosmetic procedures

The Motive Behind VNS
Why would one consider sending electrical pulses through this central nerve? The answer lies in the therapeutic benefits VNS offers. Originally developed to treat epilepsy, VNS has expanded its medical repertoire to include treatment-resistant depression and even chronic pain. The idea is simple: by modulating the activity of the vagus nerve, we can indirectly influence the parts of the brain linked with mood, pain perception, and seizure activity.
Conditions Treated by Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
1. Epilepsy:
Most popular procedures in
Laparoscopic Cystect
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Laparoscopic Myomect
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
LAVH
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
NOTE
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
CABG
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
- Used primarily for individuals who don't respond to traditional seizure medications.
- Demonstrated to decrease the frequency and intensity of seizures.
- Especially beneficial for those who are not candidates for other surgical treatments for epilepsy.
2. Treatment-Resistant Depression:
- Targeted for patients who haven’t responded to traditional antidepressant therapies.
- Studies have shown VNS can lead to significant mood improvements.
- Provides a potential alternative for those who've exhausted other treatment options.
3. Chronic Pain:
- Emerging evidence suggests VNS may be beneficial for certain chronic pain conditions.
- Mechanisms include potentially altering pain pathways or reducing inflammation.
- Still in the early stages of research but showing promise in select patient groups.
4. Other Emerging Applications:
a. Headaches:
- Some studies suggest VNS can reduce the frequency and intensity of certain types of headaches, including cluster headaches.
b. Autoimmune Conditions:
- Early research is looking into the potential of VNS to modulate the immune system, potentially benefiting conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Based on the premise that the vagus nerve plays a role in inflammation regulation.
A Closer Look at the VNS Procedure
Before the Procedure
1. Consultation and Assessment:
Purpose:
The consultation and assessment phase is the initial step to evaluate the patient's suitability for Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS). It involves a comprehensive evaluation of the patient's medical history, current health status, and seizure history.
Activities:
- Medical History Review: The healthcare team reviews the patient's medical history, including details of seizures, prior treatments, and medication history.
- Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is conducted to assess the overall health of the patient. Special attention is given to neurological examinations to understand the nature and impact of seizures.
- Diagnostic Tests: Depending on the patient's condition, diagnostic tests such as electroencephalogram (EEG) and imaging studies (MRI or CT scans) may be ordered to provide a more detailed understanding of the brain structure and seizure patterns.
- Psychosocial Evaluation: In some cases, a psychosocial evaluation may be conducted to assess the patient's mental health, cognitive function, and support systems.
2. Contraindications and Considerations:
Purpose:
Identifying contraindications and considering various factors are crucial to ensure patient safety and the effectiveness of VNS therapy.
Activities:
- Contraindications Review: The healthcare team carefully examines contraindications such as certain cardiac conditions, previous surgeries on the vagus nerve, and other medical conditions that might interfere with the successful implementation of VNS.
- Medication Review: The patient's current medications are reviewed, and adjustments may be made, especially if there are medications that may interfere with the VNS procedure or subsequent therapy.
3. Preoperative Preparation:
Purpose:
Preparing the patient for surgery and ensuring they have a clear understanding of the procedure and postoperative expectations.
Activities:
- Patient Education: The patient is educated about the VNS procedure, its purpose, potential benefits, and risks. This includes discussions about the device, possible side effects, and postoperative care.
- Medication Adjustments: If necessary, adjustments to current medications are made in consultation with the treating physician to optimize seizure control and reduce potential interactions.
- Imaging Studies: In some cases, imaging studies like MRI or CT scans are performed to assess the anatomy of the vagus nerve and surrounding structures, aiding in surgical planning.
- Informed Consent: The patient provides informed consent after receiving detailed information about the procedure, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
- Fasting and Preoperative Instructions: The patient is given specific instructions regarding fasting before the surgery and other preoperative preparations.
During the Procedure
1. Anesthesia and Patient Positioning:
Purpose:
To ensure the patient's comfort and immobility during the Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) procedure.
Activities:
- General Anesthesia: The patient is administered general anesthesia to induce a state of unconsciousness and prevent any pain or discomfort during the surgery.
- Positioning: The patient is carefully positioned on the operating table. The specific positioning may vary based on the surgeon's preferences and the patient's anatomy, but typically, the patient is placed on their back.
- Monitoring: Throughout the procedure, the patient's vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, are closely monitored to ensure their safety and well-being.
2. Surgical Insertion of the VNS Device:
Purpose:
To implant the VNS device, consisting of a pulse generator and lead wires, in the patient's body.
Activities:
- Incision: A small incision is made, usually on the left side of the chest, to create a pocket for the pulse generator. Another incision is made in the left side of the neck to access the vagus nerve.
- Subcutaneous Tunneling: The lead wires are carefully threaded under the skin from the pulse generator pocket to the incision in the neck.
- Vagus Nerve Attachment: The lead wires are then attached to the left vagus nerve in the neck. The specific attachment site may vary based on the surgeon's judgment and the patient's anatomy.
- Securing the Device: The pulse generator is placed in the subcutaneous pocket, and the incisions are closed using sutures or staples.
3. Testing and Calibration of the Device:
Purpose:
To ensure the proper functionality of the implanted VNS device and to calibrate it for optimal therapeutic effects.
Activities:
- Stimulation Testing: The surgeon performs stimulation tests to assess the response of the vagus nerve to electrical impulses. This may involve activating the device and observing any changes in heart rate, breathing, or other physiological parameters.
- Adjustment of Settings: The surgeon calibrates the settings of the VNS device, determining the appropriate stimulation parameters. This calibration is personalized for each patient based on their response to stimulation and the desired therapeutic effect.
- Confirmation of Placement: Intraoperative tests may be conducted to confirm the proper placement and functioning of the VNS device. This can involve additional imaging or monitoring techniques to ensure that the lead wires are appropriately positioned and secured to the vagus nerve.
- Closure: Once testing and calibration are complete, the incisions are closed, and the wound is dressed. The patient is then transferred to the recovery area for postoperative care.
After the Procedure
1. Immediate Postoperative Care:
Purpose:
To ensure the patient's safety and comfort immediately after the Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) procedure.
Activities:
- Recovery Room Monitoring: The patient is closely monitored in the recovery area to assess vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation.
- Pain Management: Pain management strategies are implemented to alleviate any discomfort resulting from the surgery. This may involve medications or other pain relief methods.
- Wound Care: Careful attention is given to the incision site to prevent infection. Wound care instructions are provided, and the incision site is monitored for any signs of complications.
- Neurological Assessment: Immediate postoperative neurological assessments may be conducted to ensure that there are no immediate adverse effects on the patient's neurological function.
- Patient Education: The patient and their caregivers are briefed on what to expect in the immediate postoperative period, including potential side effects and any restrictions on activities.
2. Long-Term Management and Adjustments:
Purpose:
To optimize the therapeutic effects of VNS and address any issues that may arise over the long term.
Activities:
- Follow-Up Appointments: Scheduled follow-up appointments are essential for assessing the patient's progress, monitoring device functionality, and making any necessary adjustments.
- Device Interrogation: Regular device interrogations are conducted to assess battery status, review data on seizure activity, and adjust stimulation parameters as needed for optimal control.
- Medication Management: The patient's medication regimen is often reviewed and adjusted in collaboration with their treating physician to ensure the most effective combination of VNS therapy and medications.
3. Monitoring and Follow-Up Appointments:
Purpose:
To track the patient's long-term progress, address emerging issues, and make ongoing adjustments to the VNS therapy.
Activities:
- Regular Check-ups: Scheduled follow-up appointments occur at intervals determined by the healthcare team. These appointments include device checks, neurological assessments, and discussions about the patient's overall well-being.
- Imaging Studies: Periodic imaging studies may be conducted to ensure the integrity and proper placement of the VNS device.
- Quality of Life Assessment: Evaluating the impact of VNS therapy on the patient's quality of life, including any changes in seizure frequency, severity, and the overall well-being of the patient.
- Educational Support: Providing ongoing education and support to the patient and their caregivers, addressing any questions, concerns, or challenges that may arise during the course of VNS therapy.
Latest Advancements in Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
1. Technological Improvements in VNS Devices:
- Miniaturization: Newer VNS devices are smaller, making them more comfortable for patients and less invasive to implant.
- Longer Battery Life: Enhanced battery technologies mean fewer replacement surgeries and more consistent therapy.
- Smart Calibration: Advanced algorithms allow devices to adjust stimulation based on real-time patient needs.
- Wireless Connectivity: Some devices can now connect wirelessly to monitoring systems, allowing doctors to check device status and adjust settings remotely.
2. Refinements in Surgical Techniques:
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Surgeons are now using techniques that reduce the size of incisions, leading to faster recovery and less scarring.
- Improved Electrode Design: Advances in electrode technology mean more precise stimulation and reduced potential for tissue damage.
- Real-time Monitoring: Intraoperative tools now allow surgeons to monitor the effectiveness of the device during the implantation procedure, ensuring optimal placement.
3. Advanced Research and Potential Future Applications:
- Brain-Computer Interface (BCI): Some researchers are exploring how VNS can be integrated with BCIs for advanced neurological applications.
- Mood Monitoring: With the integration of AI, future devices may predict mood changes based on physiological data and adjust stimulation accordingly.
- Expanded Medical Applications: Studies are underway to determine the effectiveness of VNS in treating conditions like anxiety disorders, PTSD, and even Alzheimer's disease.
Risks Associated with Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS)
1. Surgical Risks:
- Infection at the surgical site.
- Bleeding during or post-surgery.
- Damage to surrounding tissue or structures.
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia.
2. Device-Related Risks:
- Device malfunction, leading to inconsistent or no stimulation.
- Misfiring, which can send irregular impulses.
- Battery depletion requiring replacement.
- Potential issues with device biocompatibility.
3. Side Effects:
- Changes in voice tone or hoarseness.
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity.
- Persistent cough or feeling of a tickling sensation in the throat.
- Difficulty swallowing or discomfort in the neck region.
4. Long-Term Considerations:
- The need for regular device monitoring and adjustments.
- Possible development of tolerance, reducing the effectiveness of VNS over time.
- Risks associated with battery replacement surgeries.
- Potential interactions with other medical devices or treatments.
Results and Outcomes of VNS
Expected Benefits in Treated Conditions:
1. Epilepsy:
- Reduction in the frequency and severity of seizures.
- Improved overall quality of life.
- Potential reduction or elimination of anti-seizure medications for some patients.
2. Treatment-Resistant Depression:
- Alleviation of depressive symptoms when other treatments have failed.
- Improved mood and overall well-being.
- Potential to reduce the dosages of antidepressant medications.
3. Chronic Pain:
- Reduction in pain intensity.
- Improved mobility and functionality in daily life.
- Reduced reliance on pain medications for some patients.
4. Other Conditions:
- For emerging applications, like the treatment of headaches or autoimmune conditions, the benefits are still under rigorous study. Preliminary results show promise, but more research is needed to draw definitive conclusions.
In all cases, individual outcomes can vary based on a myriad of factors. It's always essential for patients to consult with healthcare professionals to understand the potential benefits and risks of VNS in their specific circumstances.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation, with its holistic approach, is redefining the boundaries of medical treatments. By tapping into the body's natural communication channels, VNS offers a harmonious way to alleviate several conditions. As research continues and technology advances, who knows what other wonders VNS might unveil? For now, it stands as a testament to medical innovation, offering hope to many.
This blog aims to inform and should not be taken as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making decisions about medical procedures.
Wellness Treatment
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!



