Vaginal Cancer : Symptoms to treatment
10 Oct, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamIn this blog, we'll delve into the often-neglected topic of vaginal cancer, standing as a beacon for those seeking information, support, and a community of warriors. Let's unravel the nuances of prevention, treatment, and the strength that defines every vaginal cancer survivor. Join us in breaking the silence, fostering understanding, and championing a healthier future. Because in knowledge, we find power, and in unity, we discover resilience. Let the journey begin.
Transform Your Beauty, Boost Your Confidence
Find the right cosmetic procedure for your needs.

We specialize in a wide range of cosmetic procedures

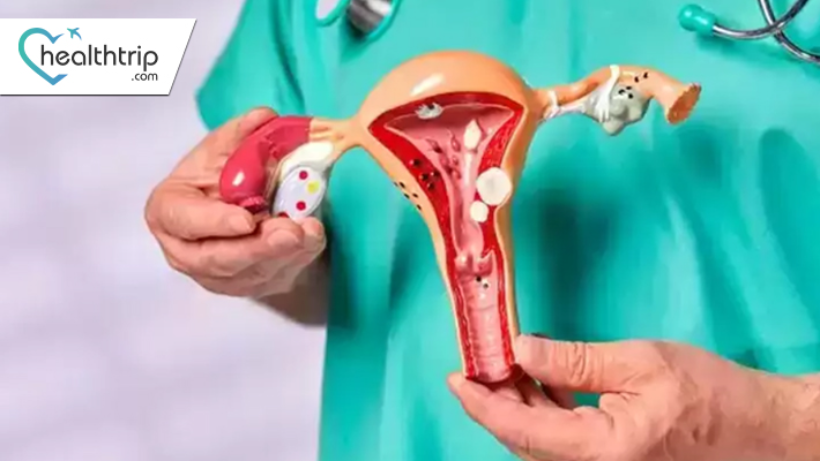
What is vaginal cancer?
Vaginal cancer is a rare type of cancer that happens in the vagina, the tube-like part connecting the uterus to the outside of the body. It can start when the cells in the vagina grow out of control. Certain things, like infections and smoking, can make it more likely. Doctors can find it with tests like Pap smears and treat it with surgery, radiation, or medicine.
Types of Vaginal Cancer
1. Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
- Squamous cell carcinoma typically originates in the thin, flat cells (squamous cells) lining the surface of the vagina.
- This type accounts for the majority of vaginal cancer cases, and its prevalence is often linked to persistent infection with certain strains of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV).
- Besides HPV, other risk factors include smoking, a weakened immune system, and age (with a higher incidence in older age groups).
2. Adenocarcinoma:
Most popular procedures in India
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
ANGIOGRAM
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

ASD Closure
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

- Adenocarcinoma arises from the glandular cells in the vaginal lining. Unlike squamous cell carcinoma, it doesn't necessarily have a strong association with HPV.
- Although less common than squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma is still a significant subtype of vaginal cancer.
- Risk factors may include exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES) in utero, age, and certain genetic conditions.
3. Sarcoma:
- Sarcoma is a rare type of vaginal cancer that forms in the connective tissues, muscles, or blood vessels of the vagina.
- It represents a small percentage of all vaginal cancers and is less common compared to squamous cell and adenocarcinoma.
- The specific risk factors for sarcoma of the vagina are not as well-established as for other types of vaginal cancer.
4. Melanoma:
- Melanoma, a type of skin cancer, can occur in the vagina. It arises from pigment-producing cells (melanocytes).
- Vaginal melanoma is relatively rare, accounting for a small percentage of all melanomas.
- Risk factors include exposure to UV radiation (though not as direct as in skin melanomas), family history of melanoma, and certain genetic factors.
Who Gets Vaginal Cancer
1. Age Groups:
- Vaginal cancer can affect women of all age groups, but it is most commonly diagnosed in women aged 60 and older.
- The risk of developing vaginal cancer tends to increase with age, emphasizing the importance of regular gynecological screenings, especially in postmenopausal women.
2. Ethnicity:
- Studies have shown variations in the incidence of vaginal cancer among different ethnic groups. While it can occur in any ethnicity, some populations may have a higher or lower risk.
- Disparities in healthcare access and utilization can contribute to differences in diagnosis rates among ethnic groups.
3. Family History:
- A family history of vaginal, cervical, or other gynecological cancers may elevate the risk. Genetic factors can play a role, and individuals with a family history should communicate this information to their healthcare providers for personalized risk assessment.
Causes of Vaginal Cancer
- HPV (Human Papillomavirus):
- Link to HPV: Persistent infection with certain high-risk strains of HPV is a major risk factor for vaginal cancer.
- Vaccination: HPV vaccination is a crucial preventive measure, offering protection against several cancer types, including vaginal cancer.
- Smoking:
- Tobacco-Related Risk: Smoking increases the risk of various cancers, including vaginal cancer. The harmful substances in tobacco may contribute to cellular changes in the vaginal tissues.
- Age:
- Increased Risk with Age: The risk of developing vaginal cancer rises with age, particularly after menopause. Regular screenings become increasingly important as women age.
Symptoms and Signs
1. Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding:
- Irregular Periods: Vaginal bleeding that is irregular, occurs after menopause, or is unrelated to menstruation may signal a concern.
- Painful Bleeding: Painful or uncomfortable bleeding during or after sexual intercourse requires attention.
2. Pelvic Pain:
- Persistent Pain: Chronic pelvic pain that doesn’t have an apparent cause should be investigated, as it can be a symptom of various gynecological issues, including vaginal cancer.
3. Pain During Intercourse:
- Dyspareunia: Pain during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia) can be an early sign. It’s crucial to discuss this symptom with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation.
4. Vaginal Lumps or Masses:
- Palpable Masses: The presence of lumps or masses in the vaginal area may indicate a tumor. Regular self-examinations can aid in early detection.
5. Changes in Bathroom Habits:
- Urinary or Bowel Changes: Vaginal cancer may cause changes in urinary or bowel habits. Symptoms can include increased frequency, urgency, or difficulty in urination or bowel movements.
Diagnosis:
1. Pap Smear:
A Pap smear, or Pap test, serves as a crucial screening procedure designed primarily for the detection of abnormal changes in the cells of the cervix and upper vagina. In this procedure, cells are delicately scraped from the cervix and upper vagina, followed by microscopic examination to identify any cellular abnormalities. While its primary use is for cervical cancer screening, Pap smears can also reveal abnormal vaginal cells, prompting further investigation.
2. Biopsy:
Biopsy, a fundamental diagnostic tool, involves the removal of a small tissue sample for meticulous examination under a microscope. Various types of biopsies may be performed, including colposcopy-guided biopsy or other methods, depending on the location and suspected nature of the abnormality. Biopsy results are crucial, providing a definitive diagnosis of vaginal cancer, specifying its type and stage.
3. Imaging Tests (MRI, CT Scans):
Imaging tests, such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans, play a pivotal role in diagnosis. These tests offer detailed images of the pelvic region, aiding in the evaluation of cancer's extent and determining whether it has spread to nearby structures. Often used in conjunction with other diagnostic methods, these imaging tests contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the situation.
4. Colposcopy:
Colposcopy, a visual examination utilizing a colposcope—a lighted magnifying instrument—is an integral part of the diagnostic process. The colposcope allows healthcare professionals to closely examine vaginal and cervical tissues for abnormalities. This procedure is instrumental in identifying and assessing suspicious areas, guiding subsequent biopsy if necessary and contributing significantly to an accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options
1. Surgery:
Surgery plays a pivotal role in the treatment of vaginal cancer by physically removing cancerous tissues. The primary objective is to eliminate the tumor and, in more extensive cases, adjacent tissues or lymph nodes that may be affected. This intervention is often crucial for achieving a complete removal of the cancerous cells and preventing further spread.
The choice of surgical procedure depends on various factors, including the size, location, and stage of the cancer. Local excision may be employed for small tumors, while radical hysterectomy is considered for more extensive cases, involving the removal of the uterus and surrounding tissues. In advanced situations, pelvic exenteration may be necessary, involving the removal of the pelvic organs.
2. Radiation Therapy:
Radiation therapy aims to destroy cancer cells or shrink tumors using high-energy rays. It is a localized treatment method that targets the affected area while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
External beam radiation delivers rays from a machine outside the body, precisely targeting the cancer site. Brachytherapy involves placing a radiation source directly inside or in close proximity to the tumor. This method allows for a more concentrated dose of radiation.
3. Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment that utilizes drugs to eradicate rapidly dividing cancer cells throughout the body. It is a versatile treatment option that can be employed as the primary therapy or in combination with other treatment modalities.
Chemotherapy drugs can be administered through oral medications or intravenously. The choice of administration depends on the specific drugs and the treatment plan designed for the individual.
4. Targeted Therapy:
Targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules involved in cancer growth and progression. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which affects rapidly dividing cells broadly, targeted therapy aims for precision in its impact.
Targeted therapy drugs are designed to interfere with specific cellular processes critical for cancer development. This precision minimizes damage to normal cells, potentially enhancing treatment effectiveness. Targeted therapy is often used when specific molecular targets are identified through genetic or molecular testing.
5. Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy harnesses the body's immune system to recognize and combat cancer cells. It represents a revolutionary approach that stimulates the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
Immunotherapeutic approaches include immune checkpoint inhibitors, which release the brakes on the immune system, adoptive cell transfer, where immune cells are extracted, modified, and then reintroduced into the body, and cancer vaccines designed to prompt an immune response against cancer cells.
How can Healthtrip help with the treatment?
If you're on the lookout for treatment in India, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, UAE, and Turkey, let Healthtrip be your compass. We will serve as your guide throughout your medical treatment. We'll be by your side, in person, even before your medical journey commences. The following will be provided to you:
- Connect with renowned doctors from a network spanning 35+ countries and access the world's largest health travel platform.
- Collaboration with 335+ top hospitals , including Fortis and Medanta.
- Comprehensive treatments from Neuro to Cardiac to Transplants, Aesthetics, and Wellness.
- Pre-scheduled specialist appointments.
- Post-treatment care and assistance.
- Teleconsultations at $1/minute with leading surgeons.
- Trusted by 44,000+ patients for appointments, travel, visa, and forex assistance.
- Access top treatments and packages, such as Angiograms and many more.
- Gain insights from genuine patient experiences and testimonials.
- Stay updated with our medical blog.
- 24/7 unwavering support, from hospital formalities to travel arrangements, emergencies.
Risk Factors:
- HPV Infection:
- Persistent infection with high-risk HPV strains increases the risk of vaginal cancer.
- Smoking:
- Smoking is linked to an elevated risk of vaginal cancer.
- Age:
- Vaginal cancer is more commonly diagnosed in older individuals.
- History of Cervical Cancer:
- A previous history of cervical cancer increases the risk of developing vaginal cancer.
- DES Exposure:
- Exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES) in utero poses an increased risk.
Complications:
- Metastasis to Nearby Organs:
- The spread of cancer to neighboring organs can complicate treatment and impact overall prognosis.
- Lymphedema:
- Fluid accumulation, known as lymphedema, may occur after treatment, particularly surgery or radiation.
- Sexual and Reproductive Issues:
- Vaginal cancer and its treatments can affect sexual function and reproductive health.
- Psychological Impact:
- Coping with a cancer diagnosis and its effects can have a profound psychological impact.
Prevention Strategies:
- HPV Vaccination:
- Provides protection against high-risk HPV strains, reducing the risk of vaginal cancer.
- Safe Sex Practices:
- Consistent use of barrier methods, like condoms, can reduce the risk of HPV transmission and other sexually transmitted infections.
- Smoking Cessation:
- Quitting smoking reduces the risk of vaginal cancer and improves overall health.
- Regular Gynecological Check-ups:
- Routine check-ups facilitate early detection and intervention, improving outcomes.
Outlook/Prognosis:
- Stage at Diagnosis:
- Prognosis varies based on the stage at which vaginal cancer is diagnosed. Early detection improves outcomes.
- Overall Health of the Individual:
- The general health and wellness of the individual impact their ability to withstand and recover from treatments.
- Follow-up Care and Monitoring:
- Regular follow-up care is crucial post-treatment for monitoring, addressing any issues, and providing ongoing support.
Early detection through screening is pivotal for improved outcomes in vaginal cancer. Stay proactive with regular check-ups, screenings, and healthy lifestyle choices to empower early detection and prevention.
Wellness Treatment
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
