
The Link Between Diet and Kidney Stones: Diagnosis and Treatment
30 May, 2023
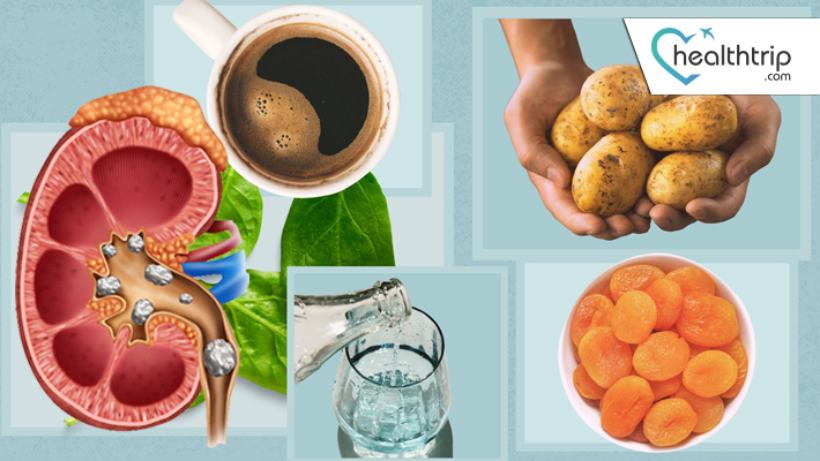
Kidney stones are a common and painful urologic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. The formation of kidney stones can be influenced by many factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and diet. In this blog, we will explore the link between diet and kidney stones, as well as the diagnosis and treatment options available for those who suffer from this condition.
What are kidney stones?
Transform Your Beauty, Boost Your Confidence
Find the right cosmetic procedure for your needs.

We specialize in a wide range of cosmetic procedures

Kidney stones are small, hard deposits of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys. These stones can range in size from tiny grains of sand to larger, more complex structures that can cause severe pain and discomfort when they pass through the urinary tract.
The symptoms of kidney stones can vary depending on the size and location of the stone, but typically include sharp, intense pain in the back, abdomen, or groin, nausea and vomiting, and difficulty passing urine. In some cases, kidney stones can cause complications such as urinary tract infections or blockages, which can lead to more serious health problems if left untreated.
How does diet influence kidney stone formation?
Diet is a significant factor in the formation of kidney stones. Some foods and beverages contain high levels of minerals and salts that can increase the risk of stone formation, while others contain substances that can help prevent the formation of stones.
One of the most common types of kidney stones is composed of calcium oxalate. Oxalate is a compound that is found in many foods, including spinach, rhubarb, nuts, and chocolate. When too much oxalate is present in the urine, it can bind with calcium to form crystals, which can eventually lead to the formation of kidney stones.
In addition to oxalate, other dietary factors can also contribute to kidney stone formation. For example, a diet that is high in animal protein can increase the excretion of calcium and other minerals in the urine, which can increase the risk of stone formation. Similarly, diets that are high in sodium can increase the excretion of calcium in the urine, which can also increase the risk of stone formation.
Most popular procedures in
Laparoscopic Cystect
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Laparoscopic Myomect
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
LAVH
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
NOTE
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
CABG
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
On the other hand, certain foods and beverages can help prevent the formation of kidney stones. For example, drinking plenty of water can help dilute the urine and reduce the concentration of minerals and salts that can lead to stone formation. Additionally, foods that are high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help regulate the digestive system and reduce the risk of stone formation.
Diagnosis of kidney stones
If you experience symptoms of kidney stones, your doctor will likely perform a series of tests to diagnose the condition. The most common diagnostic test for kidney stones is a CT scan, which can provide detailed images of the kidneys and urinary tract to identify the location and size of any stones that may be present.
In addition to a CT scan, your doctor may also perform blood and urine tests to check for signs of infection or other underlying conditions that may be contributing to your symptoms. Depending on the results of these tests, your doctor may recommend additional imaging tests or procedures to help diagnose and treat your condition.
Treatment options for kidney stones
The treatment for kidney stones will depend on the size and location of the stone, as well as the severity of your symptoms. In some cases, small stones may pass through the urinary tract on their own without the need for medical intervention. However, larger stones may require more aggressive treatment to prevent complications and relieve symptoms.
One of the most common treatments for kidney stones is extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). This procedure uses high-energy shock waves to break up the stone into smaller pieces, which can then be passed through the urinary tract more easily. ESWL is a non-invasive procedure that is performed on an outpatient basis, meaning that most patients can return home the same day.
For larger stones that cannot be treated with ESWL, other surgical procedures may be necessary. One option is ureteroscopy, which involves inserting a small, flexible scope through the urinary tract to locate and remove the stone. Another option is percutaneous nephrolithotomy, which involves making a small incision in the back to access the kidney and remove the stone directly.
In addition to these procedures, there are also several non-invasive treatments that can help prevent the formation of kidney stones in the first place. For example, medication can be prescribed to reduce the levels of certain minerals in the urine that can contribute to stone formation. Additionally, dietary changes may be recommended to help regulate the levels of oxalate and other substances in the urine.
Prevention of kidney stones through diet
Dietary modifications can be an effective way to prevent the formation of kidney stones, particularly for those who have a history of stone formation or are at a higher risk due to other factors such as family history or chronic conditions like obesity or diabetes.
One of the most important dietary recommendations for preventing kidney stones is to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water. This can help dilute the urine and reduce the concentration of minerals and salts that can lead to stone formation. In general, it is recommended that individuals drink at least eight glasses of water per day, but this may need to be increased depending on factors such as climate, activity level, and medical history.
In addition to hydration, dietary changes may also be necessary to reduce the risk of stone formation. For example, individuals who are prone to calcium oxalate stones may need to limit their intake of oxalate-rich foods such as spinach, rhubarb, and chocolate, as well as foods that are high in animal protein. Similarly, individuals who are prone to uric acid stones may need to limit their intake of purine-rich foods such as red meat, organ meats, and shellfish.
On the other hand, there are also several foods and beverages that may be beneficial for preventing kidney stones. For example, studies have shown that consuming citrus fruits and juices can help prevent the formation of calcium oxalate stones by increasing the levels of citrate in the urine, which can help prevent the formation of crystals. Additionally, consuming foods that are high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help regulate the digestive system and reduce the risk of stone formation.
Conclusion
In summary, kidney stones are a common and painful condition that can be influenced by many factors, including genetics, lifestyle, and diet. Dietary modifications can be an effective way to prevent the formation of kidney stones, particularly for those who have a history of stone formation or are at a higher risk due to other factors. If you experience symptoms of kidney stones, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to diagnose and treat the condition appropriately. By working with your healthcare provider and making appropriate dietary changes, you can take steps to reduce your risk of kidney stones and improve your overall health and well-being.
It is also important to note that prevention is key when it comes to kidney stones. While some people may be more predisposed to developing stones due to genetic factors or medical conditions, there are lifestyle and dietary changes that can be made to reduce the risk of stone formation.
One common dietary recommendation is to increase water intake, as dehydration can lead to concentrated urine and increase the likelihood of stone formation. Drinking enough water to produce urine that is pale in color is a good indicator of adequate hydration.
Another important dietary modification is reducing the intake of certain foods that may contribute to stone formation. As previously mentioned, foods high in oxalate or purines may need to be limited in some individuals. However, it is important to note that a balanced diet is still necessary for overall health and well-being. Therefore, it is best to work with a healthcare provider or registered dietitian to develop a personalized dietary plan that takes into account any medical conditions or dietary restrictions. It is also important to maintain a healthy weight and engage in regular physical activity, as obesity and a sedentary lifestyle have been linked to an increased risk of kidney stones.
Wellness Treatment
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
