Hodgkin's disease: From cause to prevention
11 Oct, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamHodgkin's disease
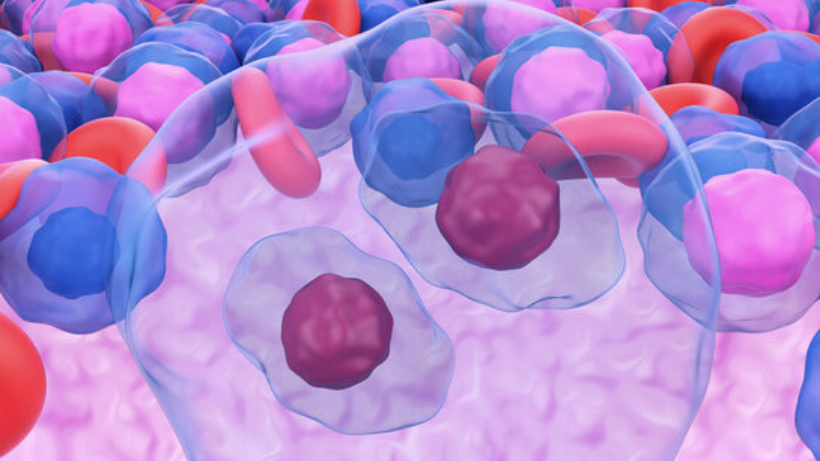
Hodgkin's disease, also known as Hodgkin lymphoma, is a type of cancer that originates in the lymphatic system. Named after Dr. Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832, this malignancy involves the abnormal growth of cells in the lymphatic system, a crucial component of the body's immune system.
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system is a network of vessels, nodes, and organs that work together to maintain fluid balance, filter harmful substances, and produce immune cells. Lymph nodes, small bean-shaped structures, are distributed throughout the body and act as checkpoints for filtering lymph fluid. The lymphatic system plays a pivotal role in defending the body against infections and diseases. Hodgkin's disease specifically targets these lymphocytes, leading to the characteristic signs and symptoms associated with the condition. Understanding the normal functioning of the lymphatic system is key to comprehending how Hodgkin's disease disrupts its delicate balance, causing health challenges for affected individuals.
Transform Your Beauty, Boost Your Confidence
Find the right cosmetic procedure for your needs.

We specialize in a wide range of cosmetic procedures

Types of Hodgkin Lymphoma:
- Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma:
- Classic Hodgkin lymphoma is the more common form, representing about 95% of all cases of Hodgkin's disease.
- Subtypes:
- Nodular Sclerosis Hodgkin Lymphoma: This subtype is characterized by the presence of nodules or bands of scar-like tissue within affected lymph nodes. It often presents in the chest area.
- Mixed Cellularity Hodgkin Lymphoma: This subtype is characterized by a mix of different cell types within the affected lymph nodes. It is often associated with the Epstein-Barr virus and commonly presents in older adults.
- Lymphocyte-Depleted Hodgkin Lymphoma: This is a rare and aggressive subtype, often found in individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS.
- Lymphocyte-Rich Hodgkin Lymphoma: This subtype is characterized by a significant number of lymphocytes and tends to have a better prognosis than other subtypes.
- Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma:
- Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma is a less common variant, accounting for about 5% of Hodgkin's lymphoma cases.
- Characteristics:
- Popcorn Cells: The characteristic cells, known as "popcorn cells" or lymphocyte-predominant cells, have a unique appearance under the microscope.
- Indolent Nature: This subtype tends to progress more slowly than classic Hodgkin lymphoma and often has an indolent course.
- Favorable Prognosis: Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma generally has a favorable prognosis, with a high cure rate even in advanced stages.
Symptoms and Signs
A. Painless Swelling of Lymph Nodes
The hallmark symptom of Hodgkin's disease is the painless enlargement of lymph nodes, often in the neck, armpit, or groin. These swollen nodes may be discovered by the individual or a healthcare professional during a routine examination.
B. Persistent Fatigue
Individuals with Hodgkin's lymphoma may experience persistent and unexplained fatigue, which is not alleviated by rest or sleep.
Most popular procedures in India
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
ANGIOGRAM
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

ASD Closure
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

C. Unexplained Weight Loss
Significant and unexplained weight loss, typically exceeding 10% of the body weight, is a common symptom of Hodgkin's disease.
D. Night Sweats
Profuse night sweats, unrelated to room temperature or external factors, are another characteristic symptom, often accompanied by drenching bedclothes.
E. Itchy Skin
Pruritus, or itching of the skin, is a symptom that some individuals with Hodgkin's disease may experience. This itching is often unrelated to any visible skin changes and can be a source of discomfort.
Causes:
- Unknown
- Possible genetic factors
- Immune system dysfunction
Diagnosis
A. Physical Examination
A thorough physical examination is often the initial step in diagnosing Hodgkin's disease. Healthcare professionals will assess for the presence of enlarged lymph nodes, particularly those in the neck, armpit, and groin. Additionally, they may examine other parts of the body for signs of the disease, such as the spleen or liver.
B. Imaging Studies (CT, PET Scans)
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan:CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the body and are valuable in detecting the extent of lymph node involvement, as well as identifying any abnormalities in nearby organs.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan:PET scans involve the injection of a small amount of radioactive material that is absorbed by active cells, including cancer cells. This helps in determining the metabolic activity of lymph nodes and aids in staging the disease.
C. Biopsy of Lymph Node or Affected Tissue
The definitive diagnosis of Hodgkin's lymphoma requires a biopsy, which involves the removal of a small sample of tissue from an enlarged lymph node or affected area. The biopsy is then examined under a microscope by a pathologist to identify the characteristic Reed-Sternberg cells, which are indicative of Hodgkin's disease.
D. Blood Tests (Complete Blood Count, Liver Function Tests)
- Complete Blood Count (CBC):CBC helps evaluate the number and types of blood cells. In Hodgkin's disease, abnormal cell counts may be observed, such as a lower-than-normal red blood cell count (anemia) or abnormal white blood cell counts.
- Liver Function Tests:Liver function tests assess the health of the liver, as Hodgkin's lymphoma can sometimes affect this organ. Abnormalities in liver function may indicate the presence and extent of the disease.
Treatment:
- Chemotherapy:
- Chemotherapy involves the use of potent drugs to target and destroy rapidly dividing cancer cells.
- Administration: Chemotherapy drugs may be administered intravenously or orally.
- Common Regimens: The ABVD regimen (doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, dacarbazine) is frequently used for Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Cycles: Treatment is typically organized into cycles, with breaks in between to allow the body to recover.
- Radiation Therapy:
- Radiation therapy employs high-energy rays to target and eliminate cancer cells.
- Local Treatment: It is particularly effective for localized disease, targeting specific areas where lymph nodes are affected.
- Side Effects: Side effects may include fatigue, skin changes, and potential long-term risks, especially if directed towards the chest area.
- Stem Cell Transplant (In Some Cases):
- Indication: Stem cell transplant may be considered for cases of refractory or relapsed Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Procedure: Healthy stem cells, either from the patient (autologous) or a donor (allogeneic), are infused to replace damaged or destroyed bone marrow cells.
- Intensification of Treatment: Allows for the administration of higher doses of chemotherapy or radiation.
- Immunotherapy (Investigational):
- Immunotherapy, using drugs like brentuximab vedotin, targets specific proteins on Hodgkin lymphoma cells.
- While not a first-line treatment, immunotherapy may be investigated in certain cases or as part of clinical trials.
- Supportive Care:
- Management of Side Effects: Medications and supportive care are provided to manage side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and immunosuppression.
- Multidisciplinary Approach: A comprehensive care team, including oncologists, nurses, and other specialists, collaborates to address the holistic needs of the patient.
Risk Factors for Hodgkin's Lymphoma:
- Age:
- Increased Risk: Hodgkin's lymphoma is more frequently diagnosed in individuals in their 20s and 30s, as well as those over the age of 55.
- Age Peaks: Two distinct age peaks are observed, with a higher incidence in young adults and another peak in older individuals.
- Family History of Lymphoma:
- Elevated Risk: Having a blood relative with Hodgkin's lymphoma elevates an individual's risk of developing the disease.
- Genetic Predisposition: There is a potential genetic component that may contribute to familial clustering.
- Gender:
- Higher Risk in Males: Individuals assigned male at birth have a slightly higher likelihood of developing Hodgkin's lymphoma compared to those assigned female.
- Past Epstein-Barr Infection:
- Associated Risk: Previous illnesses caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, such as infectious mononucleosis, increase the likelihood of developing Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Viral Connection: Epstein-Barr virus infection is linked to the development of certain lymphomas.
- HIV Infection:
- Increased Risk: People infected with HIV have a higher risk of developing Hodgkin's lymphoma.
- Immunosuppression: The compromised immune system in HIV-positive individuals contributes to the elevated risk.
Complications
- Secondary Cancers due to Treatment: Intensive treatments like chemotherapy and radiation can raise the risk of developing secondary cancers, underscoring the importance of vigilant post-treatment monitoring.
- Infertility: Fertility may be impacted by certain treatments, necessitating proactive discussions and considerations for fertility preservation options.
- Heart Problems: Some treatments, especially those involving the chest area, can pose a risk to heart health, highlighting the need for ongoing cardiovascular monitoring.
Prevention
- No Known Prevention Measures: Presently, there are no specific preventive strategies for Hodgkin's lymphoma, emphasizing the importance of awareness and early detection.
- Early Detection through Regular Check-ups: Routine medical examinations and timely diagnostic tests play a pivotal role in detecting Hodgkin's disease early, optimizing treatment outcomes. Those with risk factors should be especially vigilant and undergo regular screenings.
We can conclude In the journey through Hodgkin's lymphoma, early detection, personalized care, and ongoing follow-up prove pivotal.
Wellness Treatment
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
