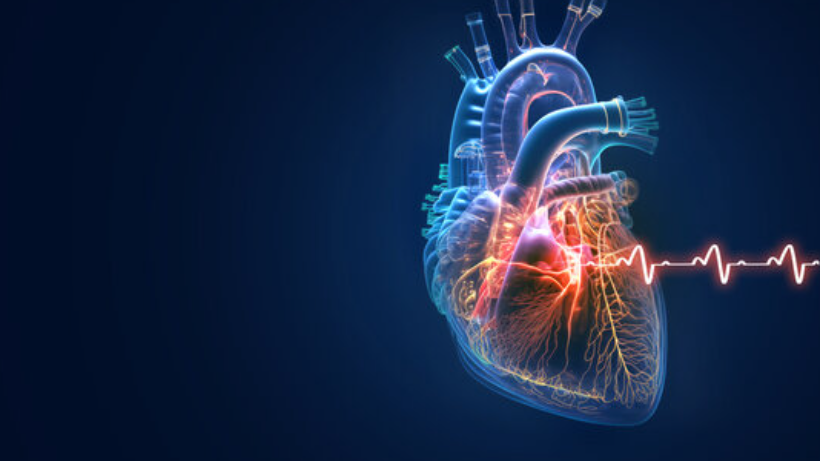
All about Congenital heart disease (CHD)
29 Sep, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamWe will discuss a critical topic that affects the lives of many individuals worldwide — Congenital Heart Disease, or CHD. This is a subject of immense importance, as it not only touches upon the intricacies of medical science but also has a profound impact on the lives of those affected and their families.
Transform Your Beauty, Boost Your Confidence
Find the right cosmetic procedure for your needs.

We specialize in a wide range of cosmetic procedures

Congenital heart disease (CHD)
Congenital heart disease refers to a group of structural and functional abnormalities present at birth in the heart and great vessels. These anomalies can affect the walls, valves, and arteries of the heart, disrupting the normal flow of blood. It's crucial to understand that congenital heart defects develop during fetal growth, often in the first eight weeks of pregnancy, when the heart is forming.
Impact of CHD:
The impact of CHD can vary widely from person to person.
Let's understand it in more detail the impact of CHD on different groups of people:
Most popular procedures in India
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
ANGIOGRAM
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

ASD Closure
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

- Infants and toddlers: Infants and toddlers with CHD may experience a number of challenges, including difficulty feeding, breathing, and sleeping. They may also need to spend long periods of time in the hospital and undergo multiple surgeries. Parents of children with CHD may also experience significant stress and anxiety.
- Children and adolescents: Children and adolescents with CHD may need to take medications and follow special dietary restrictions. They may also experience physical limitations and be more likely to be bullied by their peers.
- Adults with CHD: Adults with CHD may experience a variety of health problems, such as heart failure, arrhythmias, and stroke. They may also need to take medications and follow special dietary restrictions.
Congenital heart disease (CHD) is the most common type of birth defect, affecting about 1% of babies born worldwide each year. This means that about 1.35 million babies are born with CHD each year.
CHD can affect people of all ages, but it is most common in babies and children. About 80% of all babies born with CHD are diagnosed within the first year of life.
Despite the challenges that CHD can pose, people with CHD can live long and healthy lives with early diagnosis and treatment. However, the impact of CHD can be significant, and people with CHD may need to make lifestyle changes and take medications to manage their condition.
Types of Congenital Heart Disease (CHD): Understanding the Diverse Spectrum
1. Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD):
There's a hole in the wall that separates the lower chambers of the heart. This can make too much blood go to the lungs, and it might lead to heart problems.
2. Atrial Septal Defect (ASD):
This is when there's a hole in the wall that separates the upper chambers of the heart. It causes the mixing of different kinds of blood, and it can make the heart work harder.
3. Tetralogy of Fallot:
This is a mix of four heart problems. It includes a hole in the heart's wall (VSD), a narrow pulmonary artery, the aorta being in the wrong place, and one part of the heart getting bigger than it should. This mix can make the blood have less oxygen, causing a bluish color in the skin.
4. Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA):
After birth, a blood vessel that should close doesn't. This can cause blood to flow in the wrong way between two important blood vessels near the heart.
5. Transposition of the Great Arteries:
In this condition, the tubes that carry blood away from the heart are switched. It means the blood with and without oxygen doesn't go where it should. If not fixed with surgery, it can cause serious problems due to not enough oxygen in the body.
Understanding heart conditions can be complex, but breaking it down like this might make it a bit clearer.
There are over 40 different types of CHD, ranging from mild to severe. The most common type of CHD is a ventricular septal defect (VSD), which is a hole in the wall between the two lower chambers of the heart. Other common types of CHD include atrial septal defect (ASD), coarctation of the aorta, and transposition of the great arteries.
What are the symptoms and signs of CHD?
1. Varied Symptoms Based on the Type of CHD:
Congenital heart disease encompasses a wide range of abnormalities, each with its own set of symptoms. For instance, atrial septal defects (ASD) may manifest differently than tetralogy of Fallot. Symptoms can include but are not limited to:
- Fatigue and weakness
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Fainting or dizziness
- Cyanosis (bluish tint to the skin or lips)
- Swelling in the extremities
Infants born with CHD may exhibit specific signs that warrant attention:
- Cyanosis: Bluish discoloration of the skin or lips due to inadequate oxygenation of the blood.
- Rapid Breathing: Increased respiratory rate, which may be a response to the heart's decreased efficiency in pumping oxygenated blood.
- Poor Weight Gain: Infants with CHD may struggle to gain weight at a normal rate, reflecting the added effort required for the heart to function.
What causes congenital heart disease?
- Genetic Factors:
- Inherited Mutations: Certain genetic mutations passed down from parents may increase the likelihood of CHD.
- Chromosomal Abnormalities: Conditions such as Down syndrome are associated with an elevated risk of congenital heart defects.
- Environmental Influences during Fetal Development:
- Maternal Infections: Infections such as rubella and certain medications during pregnancy can contribute to the development of CHD.
- Maternal Conditions: Diabetes and certain autoimmune diseases in the mother may increase the risk.
- Combination of Genetic and Environmental Factors:
- Multifactorial Inheritance: In many cases, the interplay of genetic predisposition and environmental influences contributes to CHD.
- Unknown Factors: Despite advances in medical science, the exact cause of some congenital heart defects remains unknown.
How is congenital heart disease diagnosed?
- Prenatal Screening for Early Detection:
- Ultrasound Imaging: One of the primary methods for prenatal detection of CHD is through routine ultrasound examinations during pregnancy. This non-invasive imaging technique allows healthcare professionals to visualize the developing fetus and identify any structural abnormalities in the heart.
- Fetal echocardiography: In cases where there is a higher risk of CHD or if initial screening suggests potential issues, fetal echocardiography may be performed. This specialized ultrasound focuses specifically on the fetal heart to provide a detailed assessment of its structure and function.
- Diagnostic Tools:
- Echocardiograms: Postnatally, echocardiograms remain a key diagnostic tool. This imaging technique uses sound waves to create detailed pictures of the heart's structure and function. It is particularly useful in identifying the specific type and severity of congenital heart defects.
- Electrocardiograms (ECG or EKG): Electrocardiography measures the electrical activity of the heart. In the context of CHD, it helps in assessing the heart's rhythm and identifying any abnormalities. While echocardiograms focus on structure, EKGs provide insights into the heart's electrical activity.
- Cardiac MRI and CT Scans: In some cases, especially when more detailed imaging is required, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scans may be employed. These techniques provide cross-sectional images of the heart and surrounding structures.
- Physical Examinations and Medical History Assessment:
- Medical History Assessment: Gathering a comprehensive medical history, including any family history of CHD or related conditions, is crucial. Information about maternal health during pregnancy and any exposure to potential risk factors is also considered.
- Clinical Examination: A thorough physical examination by a healthcare professional may reveal signs such as abnormal heart sounds (murmurs), cyanosis, or other physical anomalies that can prompt further investigation.
How is Congenital Heart Disease Treated?
The treatment of Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) is highly individualized and depends on the specific type and severity of the heart defect. Advancements in medical science and technology have expanded the range of treatment options, offering more effective and less invasive interventions. Here are some key components of CHD treatment:
- Surgical Interventions for Structural Defects:
- Open-Heart Surgery: In many cases, especially for complex structural defects, open-heart surgery is required to repair or replace affected heart valves, close septal defects, or reconstruct abnormal blood vessels.
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Advances in surgical techniques allow for less invasive procedures, such as catheter-based interventions. These may include the use of balloons to widen narrowed vessels or the placement of stents to provide structural support.
- Medications to Manage Symptoms and Improve Heart Function:
- Diuretics: These medications help manage fluid retention and reduce the workload on the heart.
- Inotropes: Used to improve the heart's pumping ability, especially in cases of heart failure.
- Anticoagulants: To prevent blood clots, which can be a concern in certain types of CHD.
- Antiarrhythmics: Prescribed to control irregular heart rhythms.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Physical Activity: Exercise is often beneficial, but the level of activity must be tailored to the individual's condition. Regular physical activity can contribute to overall cardiovascular health.
- Nutrition: A heart-healthy diet is crucial for individuals with CHD. It may involve restrictions on salt and fluid intake.
- Regular Monitoring: Ongoing medical follow-ups and monitoring are essential to track the individual's heart function and make adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
- Interventional Cardiology Techniques:
- Transcatheter Procedures: These involve less invasive techniques to repair or treat certain heart defects. For example, transcatheter closure of septal defects or the use of devices to redirect blood flow.
- Percutaneous Valve Interventions: Techniques like transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) are becoming more prevalent, offering alternatives to traditional surgical valve replacement.
- Stem Cell Therapy and Regenerative Medicine:
- Research in Regenerative Approaches: There is ongoing research in the field of regenerative medicine, exploring the potential use of stem cells to repair damaged heart tissue in individuals with CHD. While this area is still in its early stages, it holds promise for the future.
The evolving landscape of medical science continues to bring forth innovative approaches, providing hope for improved outcomes and a better quality of life for individuals with Congenital Heart Disease. As we discuss these treatment modalities, let's acknowledge the tireless efforts of healthcare professionals and researchers dedicated to advancing the field of pediatric cardiology.
How can we help with the treatment?
If you're on the lookout for treatment in India, Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia, UAE, and Turkey, let Healthtrip be your compass. We will serve as your guide throughout your medical treatment. We'll be by your side, in person, even before your medical journey commences. The following will be provided to you:
- Connect with renowned doctors from a network spanning 35+ countries and access the world's largest health travel platform.
- Collaboration with 335+ top hospitals , including Fortis and Medanta.
- Comprehensive treatments from Neuro to Cardiac to Transplants, Aesthetics, and Wellness.
- Post-treatment care and assistance.
- Teleconsultations at $1/minute with leading surgeons.
- Trusted by 44,000+ patients for appointments, travel, visa, and forex assistance.
- Access top treatments and packages, such as Angiograms and many more.
- Gain insights from genuine patient experiences and testimonials.
- Stay updated with our medical blog.
- 24/7 unwavering support, from hospital formalities to travel arrangements or emergencies.
- Pre-scheduled specialist appointments.
- Prompt emergency assistance, ensuring safety.
Our success stories
See thousands of inspiring testimonials of Healthtrip
What are the risk factors for congenital heart disease?
- Family history of CHD
- Maternal factors during pregnancy (e.g., certain medications, infections)
- Genetic syndromes associated with CHD.
What complications can arise from CHD?
- Heart failure
- Arrhythmias
- Pulmonary hypertension
How can congenital heart disease be prevented?
- Genetic counseling for at-risk couples
- Prenatal care and screening
- Avoidance of certain risk factors during pregnancy
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) poses a significant global health challenge. Combating CHD requires a united front, integrating preventive measures, early detection, and advancements in medical interventions. Through heightened awareness, emphasis on healthy lifestyles, and equitable healthcare access, we aim to minimize the impact of CHD, fostering longer and healthier lives on a global scale.
Wellness Treatment
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!
