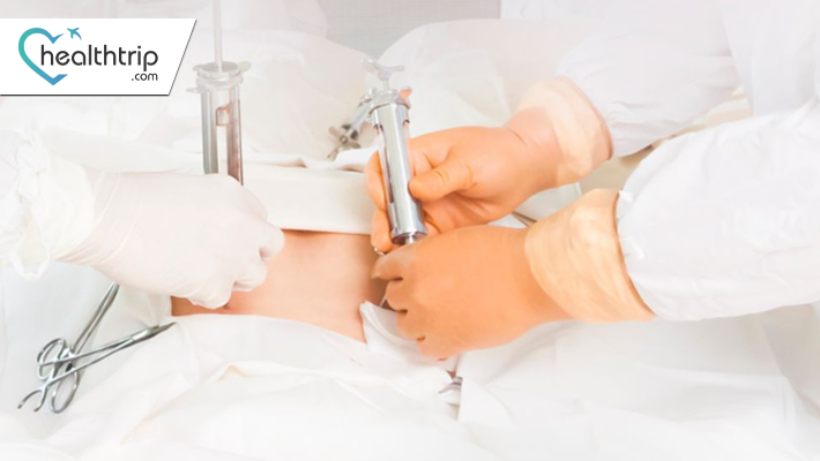
BMT (Bone Marrow Transplant): Types, Procedure, and all
26 Sep, 2023
 Healthtrip Team
Healthtrip TeamBone marrow transplant, often abbreviated as BMT, is a medical procedure that involves replacing damaged or malfunctioning bone marrow with healthy marrow stem cells. This procedure is a lifesaver for individuals grappling with a range of severe medical conditions.The importance of BMT in modern medicine cannot be overstated. It serves as a potent weapon in the battle against a variety of debilitating conditions, offering hope to patients where other treatments may fall short. Let's delve into the fascinating world of bone marrow and understand why BMT is such a game-changer.
Transform Your Beauty, Boost Your Confidence
Find the right cosmetic procedure for your needs.

We specialize in a wide range of cosmetic procedures

What is bone marrow?
Bone Marrow and Its Vital Functions: Bone marrow, the soft and spongy tissue found inside our bones, is a remarkable factory responsible for producing essential blood components. It plays a pivotal role in our overall health, ensuring a steady supply of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. These cells are indispensable for oxygen transport, immune defense, and blood clotting.
The Role of Bone Marrow in Blood Production:
Every drop of blood coursing through our veins owes its existence to bone marrow. Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells combat infections, and platelets prevent excessive bleeding. When bone marrow functions optimally, our bodies thrive.
Unfortunately, bone marrow isn't invulnerable. Various disorders and diseases can disrupt its smooth operation, necessitating a BMT. Conditions like leukemia, aplastic anemia, and certain immune system disorders can cripple bone marrow's ability to produce healthy blood cells.
Bone marrow has a diverse workforce. It produces red blood cells, vital for oxygen transport; white blood cells, the guardians of our immune system; and platelets, which maintain the integrity of our blood vessels. When any of these types of cells falter, it can lead to serious health problems.
Most popular procedures in India
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
Total Hip Replacemen
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory
ANGIOGRAM
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

ASD Closure
Upto 80% off
90% Rated
Satisfactory

Symptoms that Signal the Need for BMT
- Unexplained and severe fatigue
- Frequent and recurrent infections
- Easy bruising or uncontrolled bleeding
- Anemia, characterized by pale skin and weakness
- Persistent fever without an obvious cause
- Unexplained weight loss
- Shortness of breath and decreased exercise tolerance
- Recurrent nosebleeds and gum bleeding
- Increased susceptibility to skin rashes or petechiae (small, red or purple spots on the skin)
- Bone pain or joint pain, often severe
- Enlarged spleen or liver, leading to abdominal discomfort
- Rapid heartbeat and palpitation
Why Bone Marrow Transplants Are Done
1. Medical Conditions Requiring BMT:
Bone Marrow Transplants (BMTs) are employed as a treatment strategy for a variety of medical conditions, including:
- Leukemia: Especially when chemotherapy or radiation therapy is insufficient.
- Aplastic Anemia: When the bone marrow fails to produce enough blood cells.
- Lymphoma: In cases where chemotherapy has not been effective.
- Multiple myeloma: a bone marrow cancer that might require BMT.
- Severe Immune Deficiencies: Such as severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID).
- Inherited Metabolic Disorders: Like Hurler syndrome or adrenoleukodystrophy.
2. Alternative Treatment Options and Limitations:
While BMT is highly effective, alternative treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and medication may be considered. However, these alternatives may not provide a long-term cure or may have limited effectiveness, especially in cases of certain cancers and severe bone marrow disorders.
Types of Bone Marrow Transplants
- Autologous BMT: In this type, a patient's own healthy bone marrow or stem cells are collected, stored, and then reinfused after high-dose chemotherapy or radiation treatment. It is used in conditions where the patient's own marrow is still healthy.
- Allogeneic BMT: In allogeneic BMT, healthy bone marrow or stem cells are obtained from a donor, typically a family member or unrelated matched donor. This type is often used in cases where the patient's own marrow is compromised and a healthy donor source is needed.
- Syngeneic BMT: Syngeneic BMT is a specialized case of allogeneic transplant where the donor is an identical twin. Because the twins share the same genetic makeup, the donor's marrow is a perfect match.
- Mini-Transplants (Reduced Intensity Conditioning): Also known as non-myeloablative or reduced-intensity transplants, these are a less aggressive form of allogeneic BMT. They are used in cases where the patient may not be able to tolerate the full intensity of traditional BMT.
Benefits of Bone Marrow Transplant (BMT)
- Cure or remission for certain cancers
- Improved survival rates
- Long-term disease control
- Lifesaving treatment for non-cancerous conditions
- Restoration of healthy blood cell production
- Options for allogeneic and autologous BMT
- Utilization of umbilical cord blood
- Enhanced quality of life
Bone Marrow Transplant Procedure: Before, During, and After
Before the Procedure:
- Patient Evaluation: Extensive medical assessments are conducted to assess the patient's overall health and suitability for the transplant. This includes blood tests, imaging, and evaluations of heart and lung function.
- Donor Selection: In the case of allogeneic BMT, finding a compatible donor is critical. This involves HLA (human leukocyte antigen) matching, often with siblings or unrelated donors. Compatibility is crucial to minimize the risk of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD).
- Conditioning Regimen: Before the transplant, patients typically undergo a conditioning regimen. This involves high-dose chemotherapy and sometimes radiation therapy. The purpose is to destroy existing bone marrow and cancer cells to prepare the body for the new stem cells.
- Stem Cell Collection: If it's an autologous transplant, the patient's own healthy stem cells are collected, processed, and stored. For allogeneic transplants, donor stem cells are collected through apheresis or bone marrow aspiration.
During the Procedure:
- Infusion of Stem Cells: On the day of the transplant, the collected stem cells are infused into the patient's bloodstream, often through a central venous catheter. This process is similar to a blood transfusion and usually takes a few hours.
- Engraftment: After the infusion, the stem cells travel to the bone marrow, where they begin to grow and produce new blood cells. This period is known as engraftment and can take several weeks.
After the Procedure:
- Isolation and Monitoring: Patients are typically kept in a specialized transplant unit where they receive meticulous care. During this time, they are at heightened risk of infections due to weakened immune systems, so strict isolation procedures are observed.
- Managing Side Effects: Patients may experience side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and mucositis (inflammation of the mucous membranes). Medications and supportive care are provided to manage these side effects.
- Preventing Graft-versus-Host Disease (GVHD): In allogeneic transplants, efforts are made to prevent or manage GVHD, where the donor's immune cells attack the recipient's tissues. Immunosuppressive drugs are often administered for this purpose.
- Recovery and Follow-Up: The recovery process can be lengthy, and patients may require ongoing medical care and monitoring for several months or even years. Regular follow-up appointments are essential to track progress and address any complications.
- Immune System Reconstitution: Over time, the new bone marrow begins to produce healthy blood cells, and the patient's immune system gradually recovers. The timeline for this varies among individuals.
- Psychological Support: Patients and their families often receive counseling and support to cope with the emotional and psychological challenges associated with the transplant, including anxiety, depression, and the uncertainty of the outcome.
Preparing for a Bone Marrow Transplant:
- Medical Evaluations: Get thorough check-ups and tests to ensure you're physically ready.
- Donor Search (Allogeneic BMT): Find a compatible donor, often a sibling or unrelated match.
- Psychological Prep: Talk to a counselor to cope with the emotional aspects.
- Multidisciplinary Team: A team of experts supports you throughout the process.
- Emotional Support: Lean on support groups and mental health resources for emotional strength.
Diet and Nutrition in Bone Marrow Transplants:
1. Pre-transplant:
Focus on a balanced diet to build strength and immunity. High-protein, nutrient-rich foods are key.
- Lean meats (chicken, turkey, fish)
- Eggs
- Dairy (yogurt, milk)
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa)
- Fruits and vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
2. During Transplant:
Patients often have dietary restrictions due to weakened immune systems. Special diets may be necessary to minimize infection risks.
- Aseptic (germ-free) foods
- Well-cooked, peeled fruits and vegetables
- Avoiding raw or undercooked meats
- Limited fresh salads and unprocessed foods
3. Post-Transplant:
Gradually transition to a regular diet. Emphasize fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and hydration. Monitor for dietary complications like graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Consult a dietitian for personalized guidance.
Road to Recovery and Aftercare Following Bone Marrow Transplant:
- Initial Recovery in Hospital: Patients spend weeks in specialized transplant units, closely monitored for complications like infections and graft failure.
- Immune System Reconstitution: Over time, the new bone marrow rebuilds the immune system, but this process can take months to years.
- Long-Term Follow-Up Care: Regular check-ups and monitoring continue for an extended period to track progress and address any issues.
- Managing GVHD: Coping with Graft-Versus-Host Disease (GVHD) may require immunosuppressive drugs and other treatments.
- Physical Therapy and Exercise: Vital for regaining strength and mobility after transplant; tailored programs help prevent muscle atrophy.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining good nutrition, staying hydrated, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol support overall recovery and long-term health.
Read more : A Perfect Guide to BMT Cost in India
Risks and Complications of Bone Marrow Transplant:
- Infection Risks:
- Weakened immune system post-transplant increases susceptibility.
- Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections are common concerns.
- GVHD (Graft-Versus-Host Disease):
- Donor immune cells attack recipient's tissues.
- Affects skin, liver, and digestive tract; can be severe.
- Graft Failure:
- Transplanted cells may not engraft and produce blood cells effectively.
- Organ Damage and Secondary Malignancies:
- Conditioning regimen can harm organs.
- Slight risk of developing new cancers.
- Psychological and Emotional Challenges:
- Anxiety, depression, and adjustment difficulties are common.
- Regular follow-up and Monitoring:
- Crucial for early detection and management of complications.
- Monitoring immune system recovery and overall health.
How can we help with the treatment?
If you're on the lookout for bone marrow transplants in India, let Healthtrip be your compass. We will serve as your guide throughout your medical treatment. We'll be by your side, in person, even before your medical journey commences. The following will be provided to you:
- Connect with renowned doctors from a network spanning 35+ countries and access the world's largest health travel platform.
- Collaboration with 335+ top hospitals , including Fortis and Medanta.
- Comprehensive treatments from Neuro to Cardiac to Transplants, Aesthetics, and Wellness.
- Post-treatment care and assistance.
- Teleconsultations at $1/minute with leading surgeons.
- Trusted by 44,000+ patients for appointments, travel, visa, and forex assistance.
- Access top treatments and packages, such as Angiograms and many more.
- Gain insights from genuine patient experiences and testimonials.
- Stay updated with our medical blog.
- 24/7 unwavering support, from hospital formalities to travel arrangements or emergencies.
- Pre-scheduled specialist appointments.
- Prompt emergency assistance, ensuring safety.
Our Patient Success stories
Closing Thoughts
In closing, bone marrow transplantation represents not only a medical procedure but also a journey of resilience and hope. It offers a chance for patients to overcome life-threatening conditions and embrace a new lease on life. With the support of healthcare professionals, the unwavering strength of patients and their families, and the potential for community involvement, the path to recovery becomes a collective endeavor that highlights the remarkable power of human compassion and determination in the face of adversity.Wellness Treatment
Give yourself the time to relax
Lowest Prices Guaranteed!

Lowest Prices Guaranteed!





